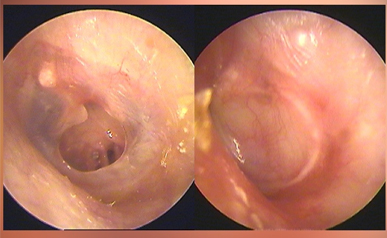
Tympanoplasty
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to repair a perforation or hole in the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and, in some cases, to reconstruct the small bones of the middle ear. The surgery helps restore hearing and prevent recurrent ear infections. It is usually recommended when a damaged eardrum does not heal on its own or when there is chronic ear discharge that does not respond to medications.