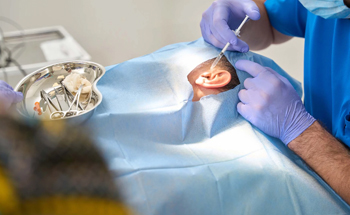
Endoscopic Ear Surgery
Endoscopic Ear Surgery is a modern, minimally invasive technique used to diagnose and treat various middle and inner ear conditions. Using a thin, high-definition endoscope inserted through the ear canal, the surgeon can perform procedures without making large incisions behind the ear. This advanced method provides a clearer view of the ear structures, reduces tissue damage, shortens recovery time, and offers excellent cosmetic results.