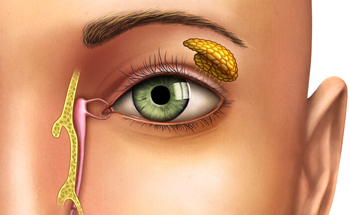
Endoscopic DCR (Dacryocystorhinostomy)
Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy (Endoscopic DCR) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat blocked tear ducts (nasolacrimal duct obstruction). The surgery creates a new passage between the tear sac and the nasal cavity, allowing tears to drain normally and relieving symptoms such as constant watering, discharge, or infection of the eye. Unlike conventional DCR, the endoscopic approach is performed through the nasal cavity — leaving no external scars and ensuring quicker recovery.