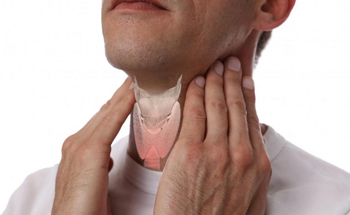
Thyroid Management & Surgery
Thyroid Management & Surgery involves the diagnosis, medical treatment, and surgical management of disorders affecting the thyroid gland — a butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of the neck that regulates metabolism, growth, and energy levels. Thyroid problems may include goiter (enlargement), nodules, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or thyroid cancer. Treatment depends on the specific condition and may include medications, radioactive therapy, or surgery when necessary.