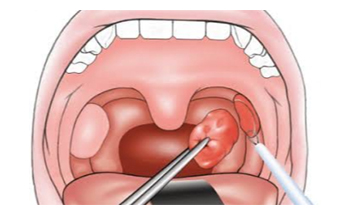
Coblation Surgery
Coblation (short for “Controlled Ablation”) is a modern, minimally invasive surgical technique used to treat various ENT conditions involving the nose, throat, and tonsils. It uses radiofrequency energy combined with saline solution to create a plasma field that gently dissolves or shrinks soft tissue at low temperatures. Coblation minimizes tissue damage, reduces bleeding, and promotes faster healing compared to traditional surgical methods.